How To Treat An Animal With Antibiotocs
Antibody Resistance and the Role of the Beast Health Industry
Antibody resistance is an important public wellness issue that all sectors using antibiotics must piece of work together to accost. The brute health industry is committed to protecting the health of animals and people by producing safe food and animal products. Antimicrobial stewardship is important to prevent, control and treat bacterial illnesses in animals. In beast health nosotros are committed to promoting scientific discipline-based policies that heighten antimicrobial stewardship and to working with veterinarians and food producers to implement good stewardship practices.
Antibiotics used in food animals are strictly regulated both earlier and after products are approved. We have worked collaboratively with FDA to implement judicious utilise practices and have made public pledges to keep to find means to meliorate manage the apply and demand for antibiotics in animals. We support efforts by the federal government to collect useful, science driven information about animal health, antibiotics and antibiotic resistance.
Dr. Melinda McCall; addresses veterinarian continuum – education, prevention, treatment, with ABX as last line (2015)
Overview
Antibiotics and antibody resistance
Antibiotics are medicines that have activity confronting bacteria. They may office by either killing the bacteria (bactericidal) or by inhibiting the growth and proliferation of bacteria (bacteriostatic) assuasive the animal's immune system to more effectively fight a bacterial infection. In either instance, the lesser line is that an antibiotic treatment stops the growth of a bacterial infection so the host (i.e. the brute) can eliminate it. The animal tin then recover and render to health.
LEARN MORE
There are several 'classes' of antibiotics. Penicillins, tetracyclines and macrolides are some common classes of antibiotics. Some are constructive confronting a wide range of bacteria (broad spectrum), while others may target merely a small set of bacteria (narrow spectrum). Some types can be used in both people and animals, while some are only useful and approved in animals or people. The term 'medically important' can refer to antibiotic classes of import to human medicine. This categorization of importance has been defined past the FDA. A subset of these antibiotics is also important to beast medicine. Many antibiotics important to human medicine are not used in animals. Additionally, there are other antibody classes used in animal medicine (eastward.g., ionophores) that are non used, nor are they of import to homo medicine. A divide listing of antibiotic classes important to animal medicine has been divers by the OIE.
An antibiotic will kill or inhibit the growth of leaner that are susceptible to information technology. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) to antibiotics occurs when the affliction-causing leaner modify in some way to reduce or eliminate the effectiveness of the antibiotic used to treat infections. Sometimes leaner have natural, or inherent, properties that make them resistant to an antibiotic. The business organisation is for those bacteria that are inherently susceptible to an antibiotic only then learn genes that enable them to withstand the effects (be resistant to) that same antibiotic. Leaner can acquire a resistance to one or more types of antibiotics merely all the same be susceptible to other types of antibiotics.
The public wellness concern occurs when an animal or homo illness is caused by bacteria that are resistant to so many antibiotics that the veterinarian or dr. cannot treat the patient with an antibody that will be constructive.
Antibiotics are and so important in treating many mutual and serious diseases that antibiotic resistance is considered ane of the biggest global health emergencies. If it is non properly managed, it could put unremarkably used antibiotics at run a risk and turn minor, treatable infections into major, lasting health threats. There are also fears that bacterial infections will acquire multiple resistance mechanisms, leaving no antibiotic treatment options that can exist used successfully for some patients.
AMR tin be a threat to both animals and people. Many bacterial diseases are zoonotic, meaning that these diseases can exist passed dorsum and forth betwixt people and animals. As a outcome, strategies to contain AMR need a "One Health" arroyo, significant physicians and veterinarians must work together to address the challenge of antibody resistance.
Responsible antibiotic use is a means to manage AMR and preserve these medicines for the time to come. It is important to always exercise the best possible antimicrobial stewardship, and the animal health industry is committed to providing veterinarians with the most electric current information nearly antibiotic products to allow them to make the advisable stewardship decisions.
Antibody Apply in Animals and People
Why and how are antibiotics used
Animals are vulnerable to some of the same bacterial infections as people, such as pneumonia and skin infections, and can be treated with antibiotics. Just similar in people, antibiotics are used in animals to treat, control and prevent diseases.
LEARN More
Many diseases spread by ticks tin touch both animals and people. Antibiotics are often given to treat these infections, which can be chronic and cause severe illness.
At that place are life stages when the adventure of bacterial infection is college. Like in people, a young animal is more than likely to succumb to an illness because their allowed organization is still maturing. Also, times of stress lower the body's defenses and an infection is more likely to occur. Examples of times of stress in an animal'southward life include transportation or change in location, rapid change or farthermost weather or following surgery. For this reason, farm animals may more likely require antibiotics at sure times in their lives whether to care for an existing infection or to command the spread of a bacterial disease within a group of animals. Farmers and veterinarians work together to forestall these occurrences and create and maintain healthy weather for their flocks and herds. They are constantly working to improve biosecurity, vaccinate and prefer other management techniques to maintain a healthy herd and proceed their animals from getting ill. Despite these efforts, disease threats still occur, and veterinarians demand access to antibiotics to address illnesses and protect the welfare of the private and the herd.
How an antibiotic is given to a patient, whether a person or an animal, is called the "route of assistants." Antibiotics for animals can be administered in the aforementioned way every bit for people: orally or via an injection.
Administering antibiotics to animals can exist challenging. While a person can usually have individual responsibleness for their medicine, animals must exist treated by a person. Anyone with a pet knows that administering a medicine to an creature tin be a challenge. And there are applied considerations when administering antibiotics to large groups of farm animals.
When there is a illness affecting a large group of animals, veterinarians must utilize group treatment, meaning administering antibiotics through either feed or water to be certain the animals are receiving the handling. In this case, the veterinary uses information about the farm, size, and weight of the animals, and feeding government to recommend the amount of medicated feed or h2o to provide to ensure a proper dosage. Then, to appropriately administer an antibody a farmer must ensure his animals get the right amount of dose at the right time and frequency without causing the animal unnecessary stress.
Blessing and Regulation of Animal Antibiotics
Like antibiotics for humans, antibiotics for animals are heavily regulated
The FDA reviews and approves brute medicines using the same standards and processes as those used for human medicine.
Larn More than
Companies seeking approval of antibiotics for animals submit data to FDA demonstrating that the production meets three standards:
- Ensure the production is condom. Rubber, co-ordinate to FDA, includes prophylactic to the animals, safety of food products derived from the animals, prophylactic to persons administering the drug or otherwise associated with the animals, and safety in terms of the drugs bear on on the surroundings.
- Ensure the product is efficacious. A product sponsor provides information for FDA review and concurrence to demonstrate that the product is rubber for the proposed claim or indication.
- Ensure that a quality product is manufactured. Quality ways the visitor adheres to the Good Manufacturing Principles and demonstrates an ability to consistently provide a stable product that is uniform in potency.
These requirements apply to all products canonical by FDA. Antibiotics require an boosted step, which is an evaluation of how use of the antibiotic might bear upon the prevalence of AMR.
Government oversight does not end with FDA approving. Three additional components to regime monitoring of antibiotics used in food animals are listed below:
- Companies must report to the FDA whatever developments in what is known about the production, including new studies that are published, new information that comes to calorie-free or any problematic reactions that develop in treated animals.
- The U.S. Department of Agriculture monitors meat for the occurrence of antibiotic residues. This monitoring plan acts as a bank check to ensure antibiotics are being used properly and to ensure the FDA-mandated withdrawal times are followed.
- The FDA operates the National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring Organization (NARMS) which tracks antibiotic resistant pathogens in samples nerveless from animals at slaughter, retail meats and people. The findings, published annually, provide information to policymakers on potential emerging resistance.
The FDA approves all claims (what it is used for) and directions (how it is used) that are on the product characterization. FDA approves antibiotics with one of 3 claims:
- Illness treatment – the administration of antibiotics to ill animals to resolve disease in the individual and(or) treatment of outbreaks within the unabridged herd or flock.
- Disease control – administration to groups of animals to contain the spread of a disease when some animals in the flock or herd become sick and expose the residual of the animals to a bacterial pathogen.
- Affliction prevention – administration when animals are not sick but there is sufficient history or risk of affliction to warrant therapy under the direction of a veterinarian.
Since the characterization also lists a specific disease or pathogen confronting which the antibiotic works, FDA has stated they consider each of these claims to be prudent and judicious therapeutic claims for the apply of antibiotics in food producing animals.
The label also contains information on the proper use of the production, such as the affliction target, the dose needed for the specific animate being co-ordinate to its weight, and the route of administration. The label may too contain restrictions or constraints on employ, such as the withdrawal time. For example, the label will include withdrawal time, or period of fourth dimension during which antibiotics may not be administered before the animate being or animate being products tin can enter the nutrient supply. The withdrawal time is mandated to ensure the meat or milk does non contain residues above limits set past FDA.
Veterinarians and Animate being Antibiotics
All medically-important antibiotics used in fauna feed and water are nether the command of licensed veterinarians.
Licensed veterinarians play an important part in antibiotic management.
Dr. Clara Nelson; addresses food supply and affliction prevention via vaccines (2016)
LEARN More
Medically important antibiotics used in feed and water for food animals all have two meaning restrictions: First, they can just exist used under the management of a licensed veterinarian using a Veterinary Feed Directive (VFD). A VFD is a course filled out by a veterinarian who has determined an antibody should be administered through an animal's feed. The VFD gives directions to a feed factory to mix antibiotics with feed, at the proper dose, and allows it to be administered to the animals. Second, antibiotics used in this manner may just exist used according to the FDA-approved directions on the label. The veterinarian cannot employ the product in an off-characterization manner, significant the dosage and utilize directions on the label must be followed exactly.
Reducing the Risk to Humans
Interventions reduce the take chances of leaner transferring from nutrient animals to people
Proven policies and procedures help reduce the possibility of bacteria transferring to people via the nutrient supply.
Larn More than
Bacteria – both resistant and susceptible – tin can pass betwixt humans and animals. The business nigh the apply of antibiotics in food animals is that this use will create pick pressure leading to resistant bacteria in the animals that tin be transferred to humans via consumption of food products from those animals.
There are many policies and procedures in place to reduce the possibility of bacteria transferring to people via the food supply. These include:
- The stringent drug approval process at FDA,
- USDA'southward Hazard Analysis/Critical Control Points (HACCP) procedures to remove pathogens in processing plants;
- The USDA residual monitoring program; and,
- Good cooking and food treatment instructions
Agriculture Doesn't Pose the Greatest Run a risk to Humans
Risk of antibody resistance is mostly due to human healthcare use
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control (CDC), overuse and misuse of antibiotics in all settings allows the development of resistant bacteria. While all uses of antibiotics tin can exert pick force per unit area for resistant organisms, inquiry shows the run a risk of antibiotic utilize in animals is extremely depression compared to uses in human healthcare settings.
LEARN MORE
In 2013 the U.S. Centers for Illness Control published a report titled "Antibiotic Resistance Threats." This certificate listed the nearly urgent bacterial resistance threats faced past doctors in human healthcare settings. Most are pathogens that don't occur in animals and thus using antibiotics in animals does non touch on the prevalence of these. A couple examples:
- One of the bacterial threats listed as "urgent" is Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) which causes life-threatening diarrhea. These infections mostly occur in people who have had both recent medical care and antibiotics. Oftentimes, C. difficile infections occur in hospitalized or recently hospitalized patients. This bacterium does not occur in animals.
- Streptococcus pneumoniae (S. pneumoniae, or pneumococcus) is the leading cause of bacterial pneumonia and meningitis in the U.s.a.. Information technology as well is a major cause of bloodstream infections and ear and sinus infections.
These are examples of serious antibiotic resistance threats that cannot be associated with animals.
In the CDC study only two of the 18 antibiotic resistant threats– Campylobacter and Salmonella are associated with farm animals. These are bacteria that unremarkably reside in the gut of animals and can brand people sick if they are consumed in raw or undercooked meat. Because these two leaner can reside in animals, they are the focus of attending and interventions by the animal health industry, producers and veterinarians. Ii studies published in Critical Reviews in Science and Nutrition focus on what is published in scientific literature about these ii pathogens:
- In 2016 a review study on Campylobacter aligned with NARMS reports, finding "contamination on most retail meats was exceedingly low." The enquiry squad constitute no conclusive evidence of a definitive link between use of antibiotics in nutrient animals and emergence of drug-resistance Campylobacter. Campylobacter infections have been linked directly to drinking raw milk or easting food products made from raw milk.
- In 2017 a like review was published on Salmonella, finding the overall prevalence of drug-resistant? Salmonella summarized in the systematic review aligned with recent National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (NARMS) reports. The 2013 NARMS written report showed that 81% of the Salmonella from man infections carried no resistance to whatever antibiotic, while Salmonella resistance rates in animals varied by the antibiotic tested. The findings of this systematic review did atomic number 82 the authors to cite important concerns nearly Salmonella and phone call for more enquiry in this area For example, six manufactures showed increased antibiotic resistance in organisms derived from animals, non retail meats, used in conventional farming, versus those from antibiotic-free operations. No studies were found that followed creature-associated antibody resistant isolates from farm to retail products.
Antibody resistance is a broad public wellness concern with many facets and cannot be adequately addressed by focusing but on animal use. Enquiry on measures to restrict use in animals in Denmark shows interventions accept not decreased resistance in primal zoonotic bacteria. Other inquiry shows that if action is simply taken in animals, AMR in people volition probable remain unchecked.
More than research is needed to fully understand the human relationship between drug resistant bacteria in people and animals. Withal, until then, we must prioritize responsible use and actions with measurable results in both animals and people.
Animal Health Industry Action on Antibiotic Resistance
The animal health manufacture is taking activity to ensure responsible antibiotic use in animals to assistance limit resistance
The animate being health manufacture works with veterinarians and producers to ensure judicious use of antibiotics in nutrient animals.
Larn MORE
The animal health industry is dedicated to working with veterinarians and producers to ensure judicious utilise of antibiotics in food animals.
Beast health companies and our merchandise associations worked collaboratively with the FDA to implement the agency'south Judicious Use Policy in 2017. Nether this policy, companies voluntarily removed growth promotion claims from medically important antibiotic compounds, leaving only therapeutic claims. As a result, antibacterial agents medically important to humans are used in food animals only to fight illness.
Likewise, equally role of Judicious Apply policy, all the antibiotics products with therapeutic claims that are used in feed and h2o were brought under the supervision of a licensed veterinarian. All medically important antibiotics added to feed must exist approved past a veterinarian past providing a Veterinarian Feed Directive (VFD), written instructions to a feed mill on how to properly mix antibiotics in the feed. The veterinary must take a Veterinary Customer-Patient Relationship (VCPR) with the producer of the animals and must brand the medical judgment that assistants of the antibiotic is needed due to disease threats or outbreaks.
In 2017, the global animal health industry released our "Commitments and Actions on Antibiotics Use." It outlines our 5 guiding principles for responsibly using antibiotics and tackling antimicrobial resistance.
We continue to demonstrate our commitment by working with the FDA on the bureau's 5-Year Plan for Supporting Antimicrobial Stewardship in Veterinary Settings. This plan includes, among other things, bringing all remaining antibiotics that are marketed over-the-counter under prescription status, thus ensuring veterinary oversight; ensuring labels on medically important compounds have appropriate duration of use instructions; collecting and analyzing data on the use of antibiotics in animals; and the evolution of a strategy to ensure antimicrobial stewardship in companion animals.
Reducing the Demand for Antibiotics
The animal health industry is committed to researching new products and ways to reduce the need for antibiotics
The animal health industry is committed to seeking new means to reduce the need for antibiotics.
LEARN More
The animal health manufacture is committed to working with veterinarians and producers to protect the health and welfare of animals. To reduce the need for antibiotic use, we focus on ways to prevent bacterial illness in the offset place.
Some of the key tools to affliction prevention are:
- Vaccines that protect animal health; animal health companies are continuously researching new vaccines to address a variety of disease threats caused by both viruses and bacteria.
- Good nutrition that bolsters an animal's immune system
- Biosecurity measures that protect animals from extreme weather condition and assist terminate bacteria from entering the subcontract
- Good fauna husbandry practices that reduce animal stress, which tin can reduce the force of an animal's immune arrangement
- Regular veterinarian visits to ensure animals are closely monitored by an expert.
New tools, such as wearable sensors and A.I. powered video monitoring, are being adopted to detect early on signs of disease. Some can even capture indications not visible to the human heart. This allows veterinarians to identify vulnerable animals earlier in the disease process. Using more authentic diagnostics – like big data applications and molecular diagnostics – veterinarians can identify the specific crusade of the affliction and target their treatment appropriately. This early intervention also allows for better isolation practices that can limit the spread of an affliction to other animals.
Despite all these efforts, animals still become sick and veterinarians need to have access to the proper antibiotics to protect animal health and welfare. Only we are working hard to assist veterinarians and producers utilise a diverseness of tools to maintain brute wellness and use antibiotics as a last resort.
Science and Data are Fundamental
Science-driven data on antibiotic utilise is needed to help inform and promote judicious practices
LEARN More than
The animal health industry believes in data. It's important for public agencies to collect science driven data on the use of antibiotics. This means at that place needs to exist a stated scientific purpose so a data collection system can be devised to reply the scientific questions. Skillful data sets should also help producers and veterinarians become more conscientious users of antibiotics.
Proficient antibody data drove would likewise cover all uses of antibiotics. Currently, no single data set exists that compares antibiotic employ levels across all sectors.
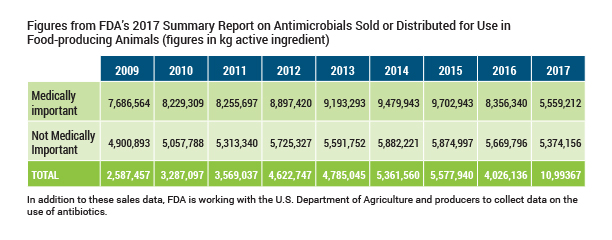
FDA, every bit required by police, collects information from companies on the amount of antibiotics sold each year for utilize in food producing animals. Sales and use are not the same, and the almanac study issued by FDA lists some cautions in interpreting the sales data presented. For example, it is inappropriate to compare the volume of creature sales to human sales or use due to the number of humans in the U.S. (320 million) versus the number of food animals (approx. ten billion) and the differences in physical characteristics of humans and animals.
The chart beneath shows sales results reported past FDA since this data collection began in 2009. Total sales declined 22 percentage in 2017 compared to 2016 and 13 percent since 2009. Sales of medically important antibiotics declined 33 per centum in 2017 compared to 2016 and 28 percent since 2009. Note that 2017 was the year that the FDA program eliminating growth promotion utilise of medically important compounds and mandating veterinary oversight for remaining uses went in effect.
[Insert Table Here]
The FDA and Judicious Utilise
Collaboration and continuous improvement contributes to strong animal wellness outcomes
The FDA, the animal health industry, and other stakeholders are making continuous improvement to ensure judicious use of antibiotics in animals.
Acquire More
In 2018 FDA announced a 5-Yr Plan for Supporting Antimicrobial Stewardship in Veterinary Settings. The program contains 32 proposed actions grouped under three broad goals:
- Align antimicrobial drug product use with the principles of antimicrobial stewardship;
- Foster antimicrobial stewardship in veterinary settings; and
- Raise monitoring of antimicrobial resistance and antimicrobial drug use in animals.
The major components of this plan relevant to the animal health manufacture are:
- Revise, as necessary, the durations of use for those medically of import antibiotic products with no defined duration: FDA/CVM recently announced a list of products affected by this objective and announced the availability of funding for data/information that would support FDA decisions.
- Motion all remaining medically of import antibiotic products from over-the-counter to prescription status.
- Revise Guidance for Industry #152, Appendix A, the listing of medically important compounds.
- Develop a strategy for promoting stewardship in companion animals.
The animal health industry will proceed to work with FDA to implement these actions in a way that ensures judicious use and protects animal wellness.
About Animal Health Institute
The Fauna Health Institute (AHI) represents the companies that develop and produce animal medicines. Our industry is a global leader whose products improve the health of nearly x billion companion and food-producing animals in the U.South., which results in significant economic and social benefits for Americans.
Resources
Problems
Source: https://ahi.org/animal-antibiotics/
Posted by: wheelerrone1950.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Treat An Animal With Antibiotocs"
Post a Comment